Data breaches are becoming one of businesses’ most common cyber threats.
In September 2022 alone, there have been two cases of data breach incidents involving big and well-known organizations, Starbucks Singapore and Singtel’s Optus.
They cost companies over $5 billion each year in lost revenue.
In 2017, the average cost of a data breach was $3.86 million, according to Verizon’s 2018 Data Breach Investigations Report.
These numbers are only going to increase as cyberattacks become more sophisticated and cybercriminals become better trained to steal valuable information.
So what can you do to help protect your business and customers from data breaches? How can you prevent data breaches from costing you billions of dollars every year?
In this article, we’re going to look at what are the causes behind data breaches and how to prevent them.
4. Ways to Prevent Data Breaches
6. How to Detect Data Breaches
7. Conclusion
What is Data Breach
We define a data breach as “any unauthorized access to personally identifiable information.”
We’re talking about the loss or theft of any of your personal information—from your name to your personal identification number to your home address and phone number—that falls into the hands of someone who shouldn’t have it.
A data breach can put a company’s reputation at risk and cause serious financial and legal problems.
According to a Forbes Insights report, 46% of organizations suffered reputational damage due to data breaches, and 19% of organizations suffered reputation and brand damage due to a third-party security breach.
Types of Data Breaches
Trojans… Worms… Spyware…Email phishing…
Sounds familiar to you?
These are just different types of data breaches that we hear of in our world today.
They come in so many different types today that we are confused by how they work and where they come from!
Before we know how to prevent data breaches effectively, it’s important to learn how to distinguish the different types.
Let’s distinguish the three most common types of data breaches we have heard of nowadays.
Phishing
Phishing scams, which entice users into giving away personal information by disguising themselves as legitimate sources such as banks or government bodies, are one of the most common types of data breaches.
This type of data breach is incredibly simple, effective, and cheap to deploy. It is one of the oldest and most effective online scams to this day.
An example of a phishing attack targeted the Covid-19 vaccine research networks in the United Kingdom in 2020 where scientists worked from home during the pandemic lockdown period.
Malware
Malware is malicious software or a malicious computer program that damages a system without the owner’s consent, and it could be used to steal personal data and destroy the system’s integrity.
It is usually installed without the user’s knowledge or consent and is designed to perform actions such as keylogging, sending spam emails, accessing sensitive information, and installing other malicious software.
Malware can infect the computer’s hard drive and corrupt files, block access to the internet, disable the anti-virus application and crash the computer. Many types of malware include viruses, Trojans, keyloggers, spyware, adware, worms, and rootkits.
Emotet has been identified as the most destructive malware by the US Department of Homeland and Security.
In 2018, it infected 450 computers at a German hospital. It mainly targets banking and health institutions.
Ransomware
Ransomware, a form of malicious software that prevents access to computers, files, and data unless the user pays a ransom to the criminal hackers that have created it, is a major problem for business owners.
Many of these ransomware attacks take advantage of software vulnerabilities in older operating systems to deliver malware through vulnerable software.
Exploiting the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, cybercriminals deployed the CovidLock ransomware. It encrypts data on an Android device and denies access to the victims unless they pay a ransom of USD 100 per device.
Causes of Data Breaches
There are three main reasons why companies experience data breaches: human error, malicious attacks, and misconfigured IT systems.
Human Error
Let’s face it.
No matter how well-designed a company’s IT infrastructure is, humans will always be prone to making mistakes.
Some examples of human error include:
- Employees accidentally delete sensitive data,
- Sending personal data to the wrong email or physical address or disclosing personal data to a wrong recipient
- Leaving laptops lying around with sensitive information on them resulting in loss or theft
- Use of weak or poor passwords
- Improper disposal of personal data
Malicious Attacks
Malicious attacks happen because attackers get access to sensitive data through social engineering or other means.
Malicious attacks can be carried out outside or from within the organization, such as:
- Unauthorized access to databases containing personal data, modification or deletion of personal data by employees
- Theft and leakage of devices or records containing personal data by a disgruntled employee
- Hacking, scams, ransomware
Misconfigured IT Systems
Verizon’s 2020 data breach report stated that software misconfiguration is on the rise.
According to an Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) annual report, there were 69% more data breaches in 2021 compared with 2020.
Configuration mistakes include both mistakes in configuring the firewall – allowing attackers to access internal systems they shouldn’t have been able to see from outside the organization – as well as cloud systems and servers that were misconfigured to allow unauthorized access.
Reasons behind the rise in misconfiguration issues could be due to the:
- Cloud misconfiguration exploits are difficult to detect using traditional security solutions
- Challenging in training team members to identify and remediate misconfiguration
- Difficulty in hiring enough cloud security experts
Famous examples of data breach cases in 2021 caused by misconfiguration are the Microsoft Power Apps data leak and the Facebook data breach.
Ways to Prevent Data Breaches
Data breach prevention has to involve everyone – not just the IT department, but every user who interacts with an IT system.
While one cannot ensure 100 percent protection against data breaches, building the right frameworks and culture goes a long way in minimizing risks.
Below are three effective ways to start putting in place part of your data breach prevention plan.
Create a Backup of Your Data
According to Enterprise Apps Today, 96% of businesses do not carry out backups. 93% of companies that experience a major data loss and do not have a recovery plan will be out of business in one year.
Make it a habit to back up your data at least once every day.
Schedule backups to occur automatically to ensure your data is automatically uploaded and saved regardless of whether you remember to perform the backup or not.
Back up your data on any external hard drives, or cloud storage and store the hard drive in a secure location, such as a safe or an offsite storage area in the event of data loss or disaster occurrence.
Here are the different technologies that companies used nowadays for backing up their data as part of their disaster recovery plans.
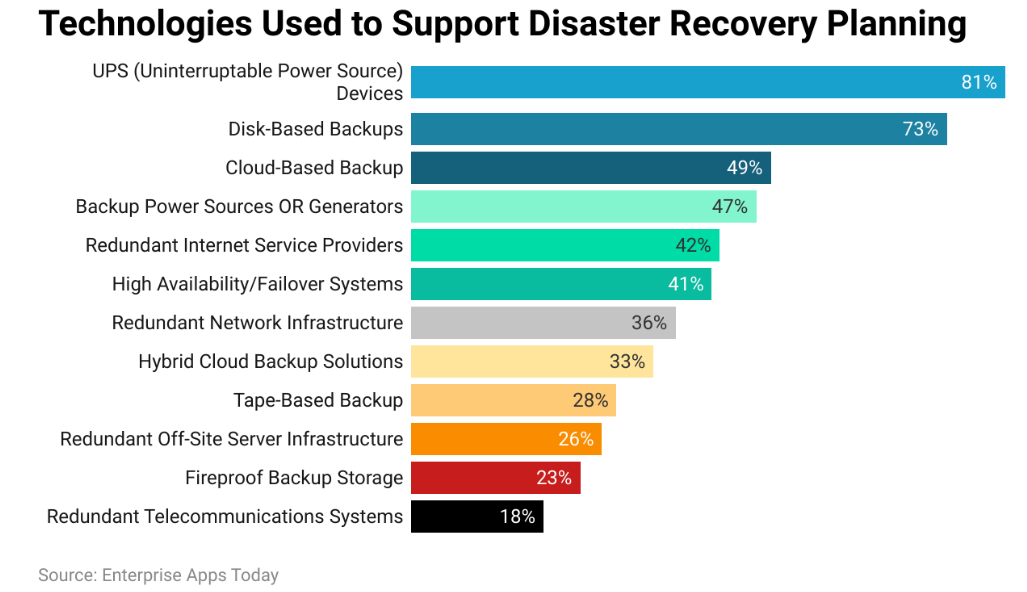
Having a backup of your data prevents your data from being held hostage by hackers.
Keep in mind that while the focus is on backing up your data, it’s also a good practice to back up your backups.
Assess Security Posture
Conduct regular assessments or audits of your assets’ level of security to identify gaps in governance and security policies.
Implement a solid information security management system (ISMS) if you don’t currently have one in place.
Identify outdated software or devices that need upgrades. Updating allows for new feature installation to offer new protection and patching security flaws as technology keeps changing.
Use compliance and vulnerability management tools to monitor for vulnerabilities that require attention.
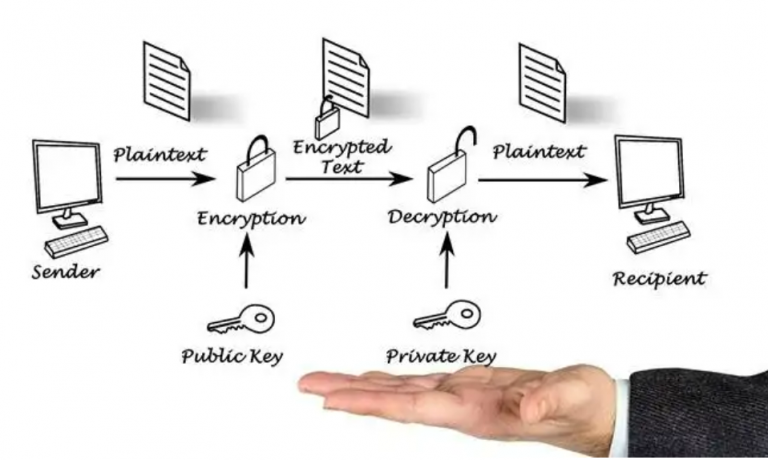
Encrypt Data
Encrypt sensitive information so that it cannot be read if it is stolen.
Encryption works by using keys that can only be deciphered by authorized users.
The easiest way to protect your sensitive data is to encrypt it on your own.
Encryption techniques can be broken down into two main categories: symmetric-key and asymmetric-key.
Symmetric-key methods include algorithms such as the Data Encryption Standard (DES) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which use a single key for both encryption and decryption. Symmetric-key methods provide only confidentiality, meaning that the data cannot be read by someone who doesn’t possess the key.
Asymmetric-key methods, including a public key and a private key, use two different keys to perform encryption and decryption. Asymmetric-key methods provide both confidentiality and integrity.
Impact of Data Breaches
Every organization has to deal with data security at some point. Whether it’s from a breach, employee negligence, or a disgruntled employee, data breaches are all too common. The cost to businesses in terms of reputation, business, and legal penalties is staggering.
When a company’s customer data is stolen, it can mean trouble for businesses in the form of lowered customer confidence, reduced profits, loss of customers, and even reputational damage.
If the breach is publicized, such as a hack attack or data leak, the effect is even worse. Consumers may take this as evidence that the business isn’t concerned about their privacy.
What it means for businesses: a data breach can affect a company’s reputation and finances greatly. Customers may remember these incidents long past they have occurred.
Any organization can be a vulnerable target of these attacks.
Two well-known organizations were targets of data breaches recently in September 2022.
“Singtel’s Optus under further fire for a cyber breach; purported hackers claim data deleted”
– The Straits Times, 27 September 2022
“330,000 S’pore Starbucks customers’ data leaked, info sold online for $3,500”
– The Straits Times, 17 September 2022
What it means for government organizations: data leaks that happen to government organizations are more severe if exposed to foreign parties. This can pose a huge threat to the government and citizens if highly confidential information lands itself in the hands of outsiders.
In 2018, the Ministry of Health (MOH) HIV registry and State Courts were affected by data breaches.
What it means for individuals: once hackers get hold of your personal information, they can use your data for all types of fraud using your name, resulting in identity theft. This can ruin your reputation, and damages can be far beyond your control.
Before all these happen, we need to be able to detect data breaches early before serious damage is done.
There are many ways in which a data breach can be detected, and let’s look at them in the next section.
How to Detect Data Breaches

Here are some ways you can learn to spot the telltale signs of cyber attacks that are going on:
1. Suspicious network activity
Your network monitoring software can alert you to suspicious network activity. These tools can scan files for malicious code and detect when unauthorized access to your data occurs. They also can monitor connections and detect any unusual behavior such as strange file transfers or log-in attempts.
For example, you can use a tool such as Netwitness Network Analyzer to view the IP addresses of all computers on your network.
This information is useful for determining whether a computer has been compromised by malware.
If you suspect that a particular computer has been infected, you can use Netwitness’s Remote Management tool to remotely access that machine and perform an offline scan of its hard disk.
You can also use a network sniffer to capture the traffic between two or more computers.
2. Suspicious banking activities
Always be on the lookout for suspicious transactions or activities that may indicate malicious acts on your account.
Alert the relevant authorities to prevent possible identity thefts.
Keep a close eye on your email and phone bills. If you notice any strange transactions, contact the bank immediately.
Get your credit card, debit card, and online banking passwords changed regularly, and do not use the same passwords for all accounts.
To avoid becoming a victim of phishing,
- Never give out your personal information to anyone
- Keep your personal identification number private
- Don’t provide your personal information when signing up for new websites
- Always call your bank before giving out any personal information if you receive a text message claiming to be from a bank
- Never use your credit card online without checking the site first
- Always verify with the company you are dealing with if you are asked to verify your ID for any reason
- Do not provide any information if you have any doubts about the request or if anything is too good to be true
3. Warnings of errors and infections
Take note of your anti-virus or anti-malware tools alerting you of system errors or warnings in browsers.
Always ensure you are using the most updated versions of your protection software.
The following can happen when a virus infects your PC:
- Your browser may not function properly, leading to errors
- Your operating system may become unstable, resulting in frequent system crashes
- Your device may stop responding to input
- Your internet connection may become unstable
- Your computer may slow down
- Your web browser may crash
4. Slow and intermittent network access
When systems are compromised by hackers accessing data, there may be unusual behavior with the internet connection. Internet speeds may be so slow or intermittent that it’s impossible to access the Internet.
When a computer is infected by malware or shows security vulnerabilities, the computer may be slower than normal. The computer may be unable to connect to certain websites.
Some network devices can provide information on what’s happening in your network. These are called Network Monitoring Devices (NMDs).
Network Monitoring Devices (NMDs) are often used by IT professionals to keep an eye on the health of their networks. They allow IT, administrators, to see what’s happening on their network from remote locations.
This is especially useful if you are unable to physically visit your office or network. There are many types of NMDs on the market. Each has different capabilities and uses.
Conclusion
As much as any company or organization would not want to be a target of cyber attacks, it’s not possible to avoid one with the growing complexities of such attacks.
No single way or method can ensure that your cybersecurity defenses are 100% foolproof.
What’s more important is to develop a comprehensive cybersecurity incident response plan so that in the event of a data breach, you would know how to handle and recover.
Continually assess and update your IT security management systems and infrastructure to keep up with the latest technological advancements and software to protect your security assets as well as update the incident response plan periodically.
Given the complexity of cyberattacks nowadays, it’s not enough to rely on antispyware or firewalls anymore.
Besides taking the precautions to guard against cyberattacks, it’s important to invest in good and sophisticated data breach detection systems to safeguard your data as well as the complexity of cyber threats increases.
Share this article if you find it useful.
Websparks is an award-winning, web solutions company. We help build websites and also provide other digital services to our clients.
Consult our experts if you need help to realise your digital dreams.